Tips and Info
LED Lighting Explained
- A Short History of LED Lighting
LED was discovered since the early days of the 20th century. LED lamps started invading markets in recent year and are expected to grow by large magnitudes in the coming years. Today's LED lighting uses a small semiconductor chip rather than a filament in a bulb to produce light.
These chips are small and compact, and they can be programmed to output different colors of light. This means that a single bulb can output blue light, white light, red light, or any other color.
- Energy Efficiency and LEDs
LEDs use far less energy than other light sources and are the greenest option in the market today. They can save energy up to 80% since they offer higher lumens/Watt compared to the previous light technologies.
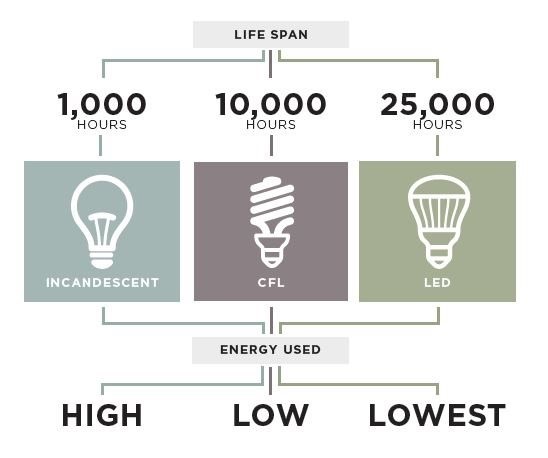
In the below chart, notice the difference in power (Watt) required to produce the same lumen lever, in this example 1,100 lumens. LEDs emit many more lumens/Watts than either incandescent bulbs or CFLs.

- LED Lifespan
LED lighting offers long life span, ranging from 8-15 years on average under optimal conditions.
This eliminates the need to constantly buy new bulbs and reduces bulbs waste thus reducing the load on landfills.

- LED Color Temperature
LED lighting offers a wide range of color tones, from the soft tone of an incandescent bulb to the bright blue tone of daylight.
These color tones are referred to as Color Temperature and their measurement is in degrees Kelvin (K).

06/03/2018
Point of Sale
TipsInfoDetails
Efficient

Environmentally Friendly

Cost Saving